Presentation
The SyCoIA unit is an independent research unit (UPR) created within IMT Mines Alès. It is the result of the merger of two groups of teacher-researchers: the “Engineering of Complex Systems Facing Risks” theme from the Risk Sciences Laboratory (LSR) and a software engineering and artificial intelligence group from the EuroMov Digital Health in Motion laboratory. SyCoIA is part of the Center for Teaching and Research in Computer Science and Systems (CERIS).

SyCoIA's scientific mission is to design and pilot intelligent systems using artificial intelligence, software engineering, systems engineering, modeling, and simulation, with a particular focus on trust, humans, and dynamic environments. SyCoIA relies on scientific platforms such as AIHM (Alès Imaging & Human Metrology) and PFM (Mechatronics Platform) for its work in human-system interaction and Industry 5.0.
The unit is heavily involved in partnership-based research (industrial chairs, Carnot, ANR, and European projects), research-based training (more than 30 doctoral students between 2019 and 2024), and international collaborations (Canada, Lebanon, Japan, Italy, etc.). SyCoIA aims to become an academic and technological benchmark in the sustainable management of complex systems, building on the strategic priorities of the Institut Mines Telecom: digital sovereignty and responsible industry of the future. The unit is involved in three IMT scientific communities: Production Systems, Trusted Digital, and Data Analytics & Artificial Intelligence
In a context marked by accelerating digital transformation, the emergence of complex cyber-physical systems, and the widespread use of artificial intelligence in decision-making processes, engineers and researchers are facing new scientific challenges: designing resilient, adaptive, explainable, and interoperable systems capable of operating in uncertain environments while respecting human, ethical, and regulatory constraints. This complexity calls for an integrated approach combining modeling, simulation, software engineering, trusted AI, and process optimization. It is with this in mind that the SyCoIA unit is building a scientific vision based on a unifying manifesto that structures the unit's ambitions in terms of research, innovation, and socio-economic partnership.
Artificial intelligence plays a central role in this transformation. It offers considerable potential for improving the planning, supervision, and operation of complex infrastructures, particularly those related to security and resilience. These systems face major challenges: climate change, energy transition, aging infrastructure, massive digitalization, and increasing complexity of value chains. For AI to be an effective lever, it must be reliable, robust, and explainable under realistic operating conditions.
These objectives cannot be achieved without rigorous engineering. Software engineering provides the necessary foundations for designing modular, secure, scalable, and interoperable systems. It also makes it possible to formalize and certify the expected behavior of software components that are sensitive to context, particularly those that integrate AI. For its part, industrial engineering provides methods and tools for analyzing, optimizing, and simulating complex processes, while taking into account resources, flows, quality, and human decision-making. It thus enables the creation of digital twins combining physical, procedural, and data-driven models, which are essential for testing and validating cyber-physical architectures in a controlled environment. In this dynamic, SyCoIA is organized around cross-disciplinary research questions that structure all of its scientific contributions:
How can we design and control complex systems capable of learning, adapting, and making decisions in a reliable, explainable, and interoperable manner in dynamic and constrained environments?
What methodological frameworks (system-software) and theoretical/applied models are necessary to guarantee the performance, robustness, traceability, and trustworthiness of these intelligent systems?
The lines of inquiry that inform the work of the SyCoIA unit have led to in-depth reflection on their operational implementation through structuring research topics. At the intersection of the scientific skills mobilized—in artificial intelligence, software engineering, systems engineering, and modeling-simulation—two research topics have been identified as unifying forces within the unit. They structure the collective scientific dynamic and enable methodological approaches to be combined with fields of application. These are:
(1) digital twins as artifacts for observing, analyzing, and optimizing systems;
(2) context-sensitive intelligent systems capable of self-adaptation and dynamic interaction with their human, technical, and informational environment.
These research questions structure the work carried out within the unit. We have considered how they can be realized through shared research topics. At the intersection of the skills and contributions of the unit's members, two unifying research topics have been identified and will be detailed in the following sections: Drawing on the expertise of its faculty in industrial engineering, software engineering, and artificial intelligence, the SyCoIA research unit has defined a manifesto in the form of a research topic, objectives, scientific skills to be implemented, and qualities to be achieved:
Design and pilot intelligent systems using approaches that integrate
artificial intelligence, software engineering, systems engineering, modeling, and simulation,
for a trustworthy digital transformation that is human-centered and adapted to dynamic and uncertain environments.
Membres
Andrade-Miranda, Gustavo, Enseignant(e)-chercheur(se), voir le CV (https://cv.hal.science/gustavo-andrade-miranda)
Ben-Ammar, Oussama, Enseignant(e)-chercheur(se), voir le CV (https://cv.hal.science/oussama-ben-ammar)
Chapurlat, Vincent, Enseignant(e)-chercheur(se), HDR, voir le CV ( https://cv.hal.science/vincent-chapurlat)
Daclin, Nicolas, Enseignant(e)-chercheur(se), HDR, voir le CV (https://cv.hal.science/nicolas-daclin)
Do, Phuc, Enseignant(e)-chercheur(se), HDR, voir le CV (https://cv.hal.science/phuc-do)
Harispe, Sébastien, Enseignant(e)-chercheur(se), HDR, voir le CV (https://cv.hal.science/sebastien-harispe)
Imoussaten, Abdelhak, Enseignant(e)-chercheur(se), HDR, voir le CV (https://cv.hal.science/abdelhak-imoussaten)
Jean, Pierre-Antoine, Ingénieur(e) de recherche
Montmain, Jacky, Enseignant(e)-chercheur(se), HDR, voir le CV (https://cv.hal.science/jacky-montmain)
Rabah-Chaniour, Souad, Enseignant(e)-chercheur(se), voir le CV (https://cv.hal.science/souad-rabah)
Ranwez, Sylvie, Enseignant(e)-chercheur(se), HDR, voir le CV (https://cv.hal.science/sylvie-ranwez)
Tchechmedjiev, Andon, Enseignant(e)-chercheur(se), voir le CV (https://cv.hal.science/andon-tchechmedjiev)
Teychene, Edith, Personnel d’appui à la recherche,
Trousset, François, Enseignant(e)-chercheur(se),
Urtado, Christelle, Enseignant(e)-chercheur(se), HDR, voir le CV (https://cv.hal.science/christelleurtado)
Vauttier, Sylvain, Enseignant(e)-chercheur(se), HDR, voir le CV (https://cv.hal.science/sylvainvauttier)
Wienin, Jean-Samuel, Enseignant(e)-chercheur(se), voir le CV (https://cv.hal.science/jean-samuel-wienin)
Zacharewicz, Grégory, Enseignant(e)-chercheur(se), HDR, voir le CV (https://cv.hal.science/gregory-zacharewicz)
Post-doctorant(e)s :
Leguy, Jules
Torres Ricaurte, Diana Maria
Sorrenti, Alessandro
Doctorant(e)s:
Alinezhad Abbas
Bhor, Tejas, thèse en cours
Chaabaoui, Layina, thèse en cours
Daou, Leonardo, thèse en cours
Daoud Charbel
Galand, Guilhem, thèse en cours
Germanos, Manuella, thèse en cours, voir le CV
Gregory, Clarissa, thèse en cours
Jabbour, Joseph, thèse en cours
Mbolamananamalala, Rindra, thèse en cours
Miemba Makita, Rolf
Saadi, Maryam, thèse en cours
Trassoudaine Loïs
Research themes
SycoIA is divided into 3 research themes :
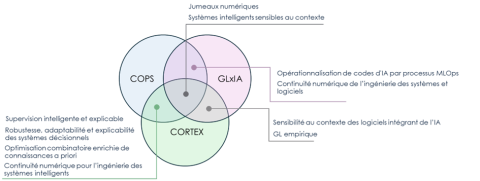
- Robustness, adaptability, and scalability of decision-making systems
- Combinatorial optimization enhanced with prior knowledge
- Digital continuity for intelligent systems engineering

Smart and Adaptive Decision Systems
- Intelligent and explainable supervision
- Robustness, adaptability, and scalability of decision-making systems
- Knowledge-based combinatorial optimization
- Digital continuity for intelligent systems engineering

- Digital twins
- Context-aware intelligent systems
- AI code operationalization through MLOps processes
- Digital continuity for systems and software engineering
- Context awareness in AI-integrated software
- Empirical software engineering

Projets emblématiques
Supported by the Institut Mines-Télécom. This strategic project aims to diversify and expand the range of AI and data science training offered at the IMT group's engineering and management schools (including IMT Mines Alès), as well as at its academic partners (ESIGELEC, UTT, CMQEs). MACMIA is building a continuum of initial and continuing education, ranging from awareness-raising at the high school level to doctoral studies, to train technicians, engineers, and managers with dual skills at the interface between AI and the industry of the future, AI and health, embedded AI and smart mobility, and AI and distribution. This project places people at the heart of digital transformation, drawing on a transdisciplinary approach and the training of new hybrid profiles, particularly cognitive engineers.
https://www.imt.fr/projet-macmia/
This European project develops solutions to strengthen the resilience of small farms in the face of crises. It incorporates technologies such as blockchain, AI, digital twins for process modeling and simulation, operational research, and digital platforms to improve traceability, market access, and resource management.
https://smallders.com/fr/
The ENFIELD project is one of Europe's major “AI Lighthouses” initiatives aimed at developing trustworthy, secure, and competitive artificial intelligence. IMT Mines Alès is contributing to this project through two areas of research. Firstly, adaptive AI: designing systems capable of dynamically adjusting to changing contexts through learning and hybrid reasoning. Secondly, human-centered AI: developing methods that promote explainability, transparency, and user trust. This project combines scientific excellence and societal challenges to strengthen European sovereignty in AI.
https://enfield-project.eu/
The CIMES (Critical Infrastructures Model-based System Engineering and Early Verification and Validation by Simulation) Chair was established to ensure continuity with the CIME Chair for an additional six years, continuing the collaboration between ASSYSTEM Engineering and Operation Services, IMT Mines Alès, and the Mines-Alès Foundation under the auspices of the Mines-Télécom Foundation. This extension and ongoing collaboration are a strong indication of ASSYSTEM's confidence and interest in funding three theses, internships, and a post-doc.
https://www.linkedin.com/showcase/chaire-industrielle-cime/
Focuses on digital twins of industrial systems and their organization. It was launched on September 20, 2023, for a renewable three-year period under the auspices of the Mines-Télécom Foundation. This chair involves three IMT schools: IMT Mines Alès, IMT Mines Albi, and Mines Saint-Etienne, as well as three industrial companies: Siemens Digital Industries Software, INOPROD, and Pierre Fabre Laboratories, all three of which have respective roles and interests in the design, deployment, and use of Digital Twins. The objective of this Chair is to design (build and execute) a responsible digital twin more quickly, i.e., one that is energy- and computing-resource-efficient and sustainable, i.e., maintainable over time using fewer resources and requiring less effort. Three theses have already been launched, one per school involved. ISOAR is working on the development of a method for engineering and maintaining Digital Twins in operational conditions based on an approach that combines Models, Data, Patterns, and Capabilities according to the intended uses.
https://digitaltwins.wp.imt.fr/
Theses
- Jacob Nimishingha AMAKAMA. Conception et mise en œuvre d'une solution interopérable d'un hôpital de campagne mobile dédié à l'industrie pétrolière et gazière. Sous la direction de Gilles Dusserre et Axelle Cadière. Accéder à la thèse : https://theses.fr/2024EMAL0003
- Nanlock Henry NIMLANG. Modélisation et prévision du risque de maladie à l'aide de la télédétection et du SIG : Application aux cas de paludisme au Nigeria. Sous la direction de Gilles Dusserre et Sandrine Bayle. Accéder à la thèse : https://theses.fr/2024EMAL0004
- Mouna EL ALAOUI. Définition d'un mode d'analyse et d'une méthodologie outillée de modélisation de la gestion des données / informations / connaissances. Sous la direction de Vincent Chapurlat et Souad Rabat Chaniour. Accéder à la thèse : https://theses.fr/2024EMAL0007
- Mariane EL KASSIS. Transformation des modèles BPMN enrichis avec des paramètres BPSim vers DEVS : Une approche incrémentale pour améliorer les processus métier par la simulation. Sous la direction de Nicolas Daclin et Gregory Zacharewicz. Accéder à la thèse : https://theses.fr/s306770
- Charbel KADY. Gestion de la Continuité et de l’Intégrité des Processus Métiers à l’aide de Corrections Basées sur des Patterns. Sous la direction de Gregory Zacharewicz et Nicolas Daclin. Accéder à la thèse : https://theses.fr/2024EMAL0014
- Tessa BONINCONTRO. Construire l'habitabilité des territoires post-miniers cévenols, entre visibilisation et invisibilisation des perturbations post-minières. Sous la direction de Pierre-Michel Riccio et Sylvia Becerra. Accéder à la thèse : https://theses.fr/2024EMAL0017
- Karim RADOUANE. Mécanisme d’attention pour le sous-titrage du mouvement humain : Vers une segmentation sémantique et analyse du mouvement interprétables. Sous la direction de Sylvie Ranwez. Accéder à la thèse : https://theses.fr/2024EMAL0002
- Rayane ELIMAM. Apprentissage automatique pour la prédiction de performances : du sport à la santé. Sous la direction de Jacky Montmain et Stéphane Perrey. Accéder à la thèse : https://theses.fr/2024EMAL0005
- AJRA Zaineb. Modèles neurophysiologiques dynamiques et apprentissage profond pour l'étude de la connectivité cérébrale de sujets sains et cérébrolésés. Encadrement de thèse : Jacky Montmain, Stéphane Perrey. Accéder en ligne : https://www.theses.fr/s296504.
- BEAUMONT Gwendal. TwinDevOps : an automated process for the deployment and dynamic evolution of digital twins. Direction de thèse : Antoine Beugnard, Sylvain Vauttier. Accéder en ligne : https://theses.fr/s370040
- Bhor, Tejas. Contribution à la définition d'une méthode de jumelage numérique en vue de l'optimisation d'un système : application à l'identification/sélection de sites en vue de l'installation d'une nouvelle centrale électrique hybride. Direction de thèse : Nicolas DACLIN, Jacky MONTMAIN. Accéder en ligne : https://theses.fr/s406691
- Bou-Slihim Jihane. Utilisation des plans d’urgence de type plan de continuité d’activités en situation de pandémie. Encadrement de thèse : RICCIO Pierre-Michel, BONY-DANDRIEUX Aurélia. Accéder en ligne : https://www.theses.fr/s262054
- Chaabaoui, Layina. Contribution méthodologique a l'utilisation de la simulation dans le cadre du déploiement de l'évaluation d'architecture pour les installations nucléaires de base. Direction de thèse : Vincent Chapurlat. Accéder en ligne : https://theses.fr/s413141
- CHAFIQ Mohamed. Planification et ordonnancement de la production centrés sur l'humain et la capture de mouvement. Direction de thèse : Oussama Ben-ammar. Accéder en ligne : https://theses.fr/s410944
- Daou, Leonardo. Contribution de l'IA générative à l'interopérabilité fédérée des organisations IAG4IO. Direction de thèse : Nicolas Daclin, Gregory Zacharewicz. Accéder en ligne : https://theses.fr/s406273
- DAOUD Charbel. PLasticité des Assistants Numériques dans les Environnements IntelligenTS (PLANETS). Direction de thèse : Christelle Urtado, Sylvain Vauttier.
- DUPUY Théo. Modèles prudents pour l'IA adaptative. Direction de thèse : Abdelhak Imoussaten, Stéphane Perrey. Accéder en ligne : https://theses.fr/s403497
- Galand, Guilhem. Construction d'un jumeau numérique d'un procédé de vitrification en vue de son pilotage. Direction de thèse : Vincent Chapurlat. Accéder en ligne : https://theses.fr/s376613
- Germanos, Manuella. Système d'aide à la décision pour la logistique de circuits courts intégrant les aspects humains et environnementaux. Encadrement de thèse : Grégory Zacharewicz, Oussama Ben Ammar. Accéder en ligne : https://www.theses.fr/s355793
- Gregory, Clarissa. Développement d'une méthodologie outillée basé sur la Maquette Numérique pour améliorer le concept de jumeau numérique des systèmes complexes : Conception, migration et maintenance. Direction de thèse : Vincent Chapurlat. Accéder en ligne : https://theses.fr/s375569
- Jabbour, Joseph. Une plateforme de modélisation et simulation distribuée pour une pédagogie immersive. Encadrement de thèse : Grégory Zacharewicz. Accéder en ligne : https://www.theses.fr/s361197
- LOPES DE SOUZA Victor. Classification prudente de la réponse individuelle à la rééducation post-AVC. Direction de thèse : Abdelhak Imoussaten, Sofiane Ramdani.
- Mbolamananamalala, Rindra. Développement d'une approche pour l'ingénierie et la maintenance de jumeaux numériques basée modèles, interopérabilité et usages. Direction de thèse : Vincent Chapurlat. Accéder en ligne : https://theses.fr/s376614
- Miemba Makita, Rolf. Transformation et simulation de modèles d’architectures pour l’analyse de la Sûreté de Fonctionnement de systèmes complexes. Direction de thèse : Grégory Zacharewicz
- OUHSSAIN Asmae. DRL2MOVE - Apprentissage profond et par renforcement pour la génération et l'analyse de mouvement humain. Direction de thèse : Jacky Montmain.
- Saadi, Maryam. Vers un pilotage d'atelier assisté par une approche mixte de Modélisation Simulation et Intelligence Artificielle. Direction de thèse : Nicolas Daclin, Grégory Zacharewicz. Accéder en ligne : https://theses.fr/s368025
- Shombot Song. Détection de cyber attaques. Direction de thèse : Gilles Dusserre.
- TALEB SALAH Nouha. Optimisation de processus de fabrication en présence de facteurs humains. Direction de thèse : Pierre Slangen, Jacky Montmain. Accéder en ligne : https://theses.fr/s367952
- UKWUOMA Henry. Détection d'intrusion dans les systèmes cyberphysiques pour une cybersécurité améliorée des systèmes de gestion de l'eau. Direction de thèse : Gilles Dusserre. Accéder en ligne : https://theses.fr/s353033
Scientific publications
Nos partenaires
The Occitanie region is fully aligned with national and European initiatives, actively supporting innovation and research in artificial intelligence, digital transformation, and the industry of the future. With a dense industrial fabric (aeronautics, energy, agribusiness, health) and ambitious support mechanisms (SRI-SI, regional calls for projects, support for industrial demonstrators, etc.), the region is fertile ground for the development of sovereign, ethical, and sustainable technologies. The projects led or supported by the Aerospace Valley, DERBI, Agri Sud-Ouest Innovation, Innovosud, and Ad'OCC clusters reflect the region's desire to structure an AI and digital twin ecosystem closely linked to the needs of strategic sectors. In this context, SyCoIA aims to play a leading role as a key academic partner for regional socio-economic players, contributing to high-impact interdisciplinary research rooted in the realities of the territories.
The unit actively participates in innovation ecosystems through competitiveness clusters such as SystemX, Minalogic, and Aerospace Valley, which bring together collaborative projects focused on digital simulation, embedded AI, and industrial optimization.
Partnership projects are also carried out with leading companies such as Airbus, Dassault Systèmes, Assystem, and Schneider Electric on strategic issues: predictive maintenance, supply chain optimization, energy efficiency, and critical infrastructure reliability.
Finally, SyCoIA contributes to the development of digital twins applied to industrial production by integrating the interoperability standards defined by the Industry 4.0 platform, in particular through the implementation of the Asset Administration Shell (AAS). This work aims to offer concrete, industrializable solutions for connected, traceable, and sustainable engineering.
APS: The Sycoia laboratory at IMT Mines Alès is pleased to confirm its partnership with APS – Agnostic Production Systems for a research collaboration within our laboratory. In this context, the work will focus on the intelligent orchestration of production systems, federated interoperability, hybrid simulation, and the use of artificial intelligence for the supervision and optimization of industrial processes. This collaboration aims to develop innovative solutions for flexible and resilient production systems.
ClicNwork : ClicNwork provides recruiters with a SaaS platform to optimize and enhance their existing candidate databases in real time and turn their HR data into performance levers.
ClicNwork's ambition is to put Artificial Intelligence at the heart of its Candidate CRM for an innovative, simple, efficient, AI-enhanced, and 100% automated CRM. As part of the incubation program at the Incubateur Mines Alès, ClicNwork called on CERIS to address the major challenges of connecting candidates with job offers in real time and leveraging candidate databases in real time to increase employability and address turnover issues. ClicNwork entrusted CERIS with conducting research as part of its algorithmic design project to automate the matching of job offers and candidates' resumes. With a candidate-centered approach, ClicNwork offers career support with a training program tailored to the candidate.
CEA, IMT Atlantique, Mines Saint-Étienne, IMT NE, IMT Mines Albi, l’Université de Bordeaux ; AFIS (Association Française d’Ingénierie Système), LaBri, IMS(Bordeaux), l’IRISA (Rennes), l’IRIT (Toulouse). LIRMM (Montpellier).
The University of Genoa; The University of Calabria, STUBA, TU WIEN, York University in Toronto. Internationally, COPS aims to strengthen its presence in European networks such as EFFRA, ITEA, and Made in Europe.
Ongoing international collaborations with Lebanon (Lebanese American University, Byblos), Argentina (Universidad Nacional de Quilmes and Universidad Austral), and Algeria (University of Blida).
LIP6 (SU), Heudiasyc (UTC), IRIT (UT), LIRMM (UM), Inria Sophia Antipolis, etc.) and internationally (AIST (Japan), RIKEN (Japan), Max Planck Florida Institute for Neuroscience (USA), ATHENA RC (Greece).
The teams' contributions to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) have both specific features and commonalities. A shared foundation emerges around SDG 9 – Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure, which is a cross-cutting theme for COPS, CORTEX, and GLxIA, illustrating their shared commitment to responsible innovation and the transformation of production systems.
The COPS team is particularly involved in energy and urban transition dynamics, in line with SDG 7 – Affordable and Clean Energy and SDG 11 – Sustainable Cities and Communities. Its work contributes to the design of more resilient and sustainable environments.
For its part, CORTEX is expanding its action to include social and governance issues. Its activities mobilize several SDGs: reducing inequalities (SDG 10), peace, justice, and strong institutions (SDG 16), as well as quality education (SDG 4) and good health and well-being (SDG 3). In addition, CORTEX is also interested in issues related to poverty reduction (SDG 1) and hunger (SDG 2), reflecting a strong societal dimension.
Finally, the GLxIA team is naturally linked to SDG 9, which is already common to all three groups, but its work also opens up prospects for sustainable economic growth and decent work (SDG 8), highlighting the central role of artificial intelligence in industrial innovation and employment.

